Dice have been an element shaping games of chance and even divination in many cultures. The history of dice is as rich and varied as the games they’ve influenced, from their early origins to their use in today’s gaming culture. Let’s explore how these small, simple objects have left a significant mark on human history.
An Overview of Dice
Dice are small, often cube-shaped objects, used in both gambling and social games to generate random outcomes.
Typically, a die has six faces marked with dots (called pips), arranged so that opposite sides always total seven (e.g., one and six, two and five).
However, not all dice follow this pattern. Variants like poker dice and crown and anchor dice feature different markings, and dice can come in many shapes, including polyhedral forms with 4, 8, 12, or even 20 sides.
The design and number of dice determine the mathematical odds in any game.
This simple yet versatile tool has been integral in games of chance for centuries, providing a universal method for creating fair and unpredictable outcomes.
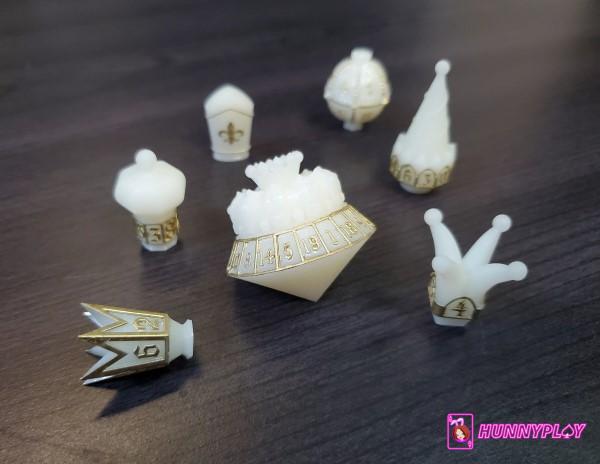

Crown dice (Source: Internet)
A Concise History of Dice
Dice are among the oldest gaming tools known, with the history of dice stretching back thousands of years.
Ancient Greek writers like Sophocles and Herodotus credited the invention of dice to figures such as Palamedes and the Lydians. However, archaeological evidence about the history of dice shows dice were used much earlier across various cultures.
Early dice-like objects were often used for divination, casting lots to predict the future.
One of the earliest forms were knucklebones (astragals), often from animals like sheep, which served as forerunners of modern dice. These bones were sometimes marked and are still used in some cultures today.
Greek, Roman and Egyptian dice
During Greek and Roman times, dice were crafted from materials like bone, ivory, bronze, and even precious stones like agate and onyx.
Ancient Chinese excavations have uncovered cubical dice from 600 BCE, while similar finds have been made in Egyptian tombs from 2000 BCE. The Mahabharata, an ancient Sanskrit epic, contains early written records of dice.

Roman-era dice
Varieties of dice
Alongside cubical dice, pyramidal dice (four-sided) were common, particularly with games like the Royal Game of Ur, dating back to Sumer around the 3rd millennium BCE. Other dice forms included the teetotum, a spinning top used in some games.
Mathematical analysis of dice
It wasn’t until the 16th century that the study of probability and randomness in dice rolls began, thanks to figures like Girolamo Cardano and Galileo. Before this, dice outcomes were often thought to be determined by gods or fate.

Ancient limestone dice from the Middle Ages closely resemble the dice we use today. (Source: Iinternet)
Key timelines of dice history
Dice have played a crucial role in human civilization, dating back thousands of years. Below are some key moments in the history of dice, from ancient Egypt to modern-day role-playing games like Dungeons & Dragons.
- 3100 BCE: Hieroglyphics of Senet boards depict two-sided pieces for randomization.
- 3000 BCE: Oldest confirmed dice discovered in Turkey, alongside game pieces.
- 2600 BCE: Pyramidal d4 dice found in the Royal Game of Ur in ancient Sumeria.
- 2000 BCE: Cubical dice unearthed in Egyptian tombs.
- 1333 BCE: Knucklebones found in Tutankhamen’s tomb.
- 900 BCE: Tuscany dice, marked with standard pips, found near Rome.
- 600 BCE: Cubical dice excavated in ancient China.
- 400 BCE: The Mahabharata records dice gameplay in India.
- 300 BCE: The oldest d20 found from Egypt’s Ptolemaic period.
- 150 BCE: A 12-sided die from Egypt’s Ptolemaic period.
- 100 AD: Roman d20 sold for $17,925 at auction in 2003.
- 1600 AD: Probability theory begins with the mathematical analysis of dice by Galileo and Cardano.
- 1888 AD: Introduction of 8-sided poker dice.
- 1906 AD: First patent for a 10-sided die in the US.
- 1974 AD: Dungeons & Dragons publishes with polyhedral dice, influencing modern dice design.
- 1980 AD: The 10-sided dice was introduced at GenCon.
- 1985 AD: The release of the Zocchihedron, a 100-sided die, marking the evolution of dice.
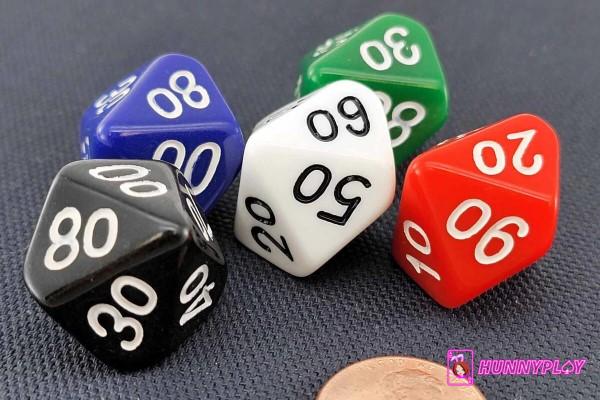

Polyhedral dices (Source: Internet)
The Manufacture of Dice
The manufacture and materials of ancient dice
When people think of dice, they often imagine a classic six-sided cube with black dots, but in the history of dice, they were far more varied.
Early dice were made from natural objects like sticks, seeds, or shells. Many were two-sided, with one flat and one rounded side, used by cultures from the Aztecs to Polynesians.
Knucklebones (astragals) were another popular type, used by civilizations such as the Romans and Egyptians. These bones, taken from large animals, had four uneven sides, making them less random and more skill-based than modern dice.
Over time, dice evolved from natural materials to carefully crafted, manufactured objects.
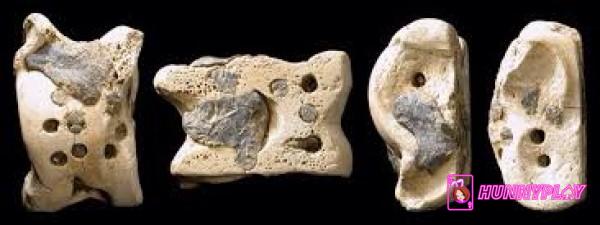
Knucklebone dice from the 5th-3rd centuries BC
The manufacture and materials of morden dice
Most modern dice are crafted from cellulose or other types of plastic. There are two primary categories:
- Casino dice (or “perfect dice”) have sharp edges and precise corners. These are hand-made to a tolerance of 0.0001 inches and are used in gambling games like craps, where accuracy is crucial.
- Round-cornered dice (or “imperfect dice”) are machine-produced with less precision. These are typically used in social games and board games, where the level of exactness isn’t as critical.
This manufacturing distinction ensures that dice fit their specific gaming purpose.
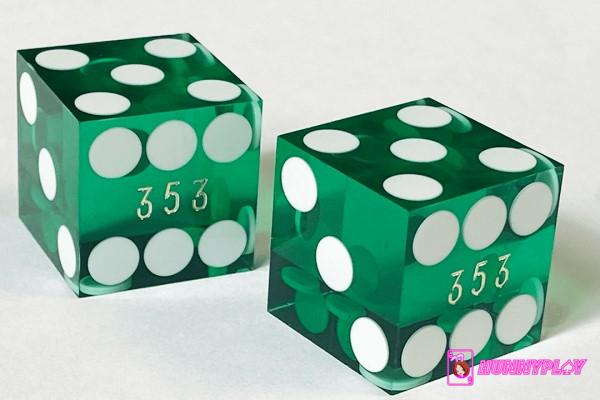

Casino dice or perfect dice (Source: Internet)
Cheating with Dice
In the history of dice, this tool was used for cheating; often called crooked or gaffed dice. It has existed since ancient times, with evidence found in Egypt, Viking graves, and beyond. Cheaters use a variety of methods to rig dice:
- Shape or Brick Dice: Dice that are not perfect cubes, such as those shaved on one side, often land on their larger faces, skewing the outcome.
- Loaded Dice: These may appear fair but have hidden weights to increase the likelihood of landing on certain numbers. Depending on where the weight is placed, they have various names like tappers or floppers.
Another technique involves tops and bottoms dice, where certain numbers are duplicated to ensure favorable outcomes in games like craps. Since players can only see three sides of a die at once, this trick often goes unnoticed.
Lastly, controlled shots allow skilled players to manipulate fair dice with techniques like the whip shot or blanket roll, which require practice and dexterity.
To combat this, casinos use slanted tables and require dice to hit the back wall, making it harder for cheaters to control the roll.

In the history of dice, they were used for cheating. (Source: Internet)
History of Dice: FAQs
Q: Who invented the dice?
A: The exact origin of dice is unknown, but the earliest known dice date back to 3000 BCE, found in the Indus Valley. Predecessors like knucklebones have been discovered in tombs in Iran from around 6000 BCE.
Q: What are some interesting facts about dice?
A: Dice are small objects used in games and divination. The word dice is plural for die. Early dice were made from knucklebones, and the modern six-sided die with pips has been the standard for thousands of years.
Q: What were ancient dice used for?
A: Ancient dice, made from items like pebbles or seashells, were used both for gaming and divination, often seen as tools for communicating with the gods.
Conclusion
The history of dice spans centuries, evolving from simple gaming tools to symbols of randomness, fate, and divine communication. They remain one of the most enduring and adaptable inventions in human history. As dice continue to be used across cultures and games, their legacy will persist, influencing generations to come. Visit HunnyPlay to read more interesting information about gambling world!




















